组内消息
2019-11-29
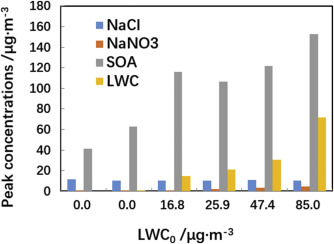
Role of liquid water in the formation of O3 and SOA particles from 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene
Highlights
• Liquid water can affect the formation of O3 and SOA from 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene.
• The hygroscopic growth factors of SOA from 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene were measured.
• Hydrolysis of N2O5 is the major reason for the decrease of O3.
• The major contribution of SOA under high LWC conditions comes from aqueous reaction.
Luo, H., Jia, L., Wan, Q., An, T., Wang, Y., 2019. Role of liquid water in the formation of O3 and SOA particles from 1,2,3-trimethylbenzene. Atmos. Environ. 217, 116955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2019.116955
组内消息
2019-05-19
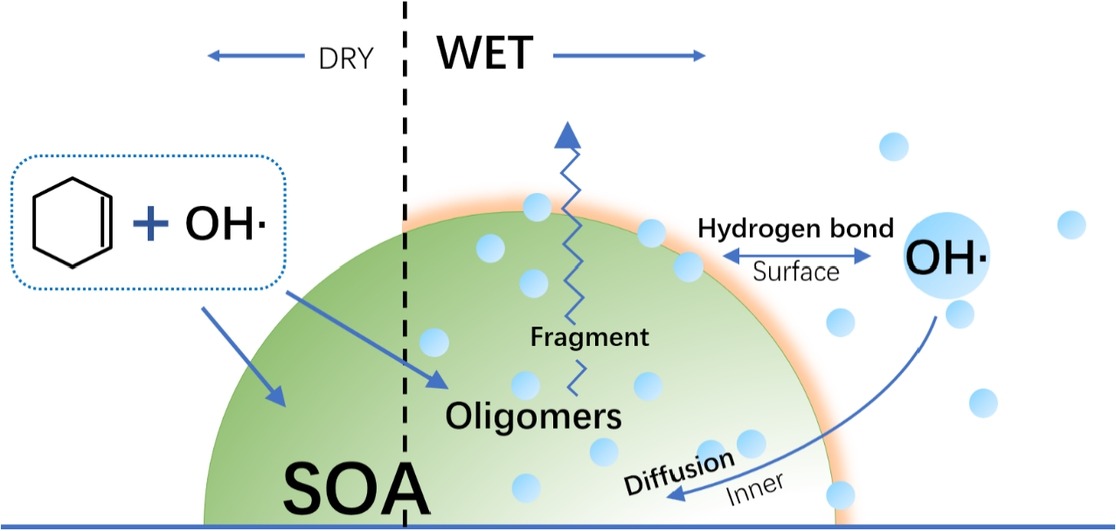
Influence of relative humidity on cyclohexene SOA formation from OH photooxidation
Highlights
• Combined effects of OH and RH on cyclohexene SOA formation were studied.
• The formation of oligomers at high RH was responsible for the increase of the SOA yield.
• High RH increases the OH uptake coefficient of SOA, and promotes SOA aging.
• Oligomers formation mechanism from cyclohexene photooxidation at high RH was proposed.
Liu, S., Tsona, N.T., Zhang, Q., Jia, L., Xu, Y., Du, L., 2019. Influence of relative humidity on cyclohexene SOA formation from OH photooxidation. Chemosphere 231, 478–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.131
Full text:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.05.131
组内消息
2019-02-19
Short Summary: The significantly negative effects of relative humidity (RH) on secondary organic aerosol (SOA) formation from m-xylene under low NOx conditions were observed. The significant RH effects on chemical compositions of SOA are identified, in which highly oxygenated molecules (HOMs) are dominant. Our results show that the decrease of SOA formation under high RH conditions is mainly attributed to the suppression of the formation of oligomers and HOMs.
Zhang, Q., Xu, Y., and Jia, L.: Secondary organic aerosol formation from OH-initiated oxidation of m-xylene: effects of relative humidity on yield and chemical composition, Atmos. Chem. Phys., https://www.atmos-chem-phys.net/19/15007/2019/acp-19-15007-2019.html, 2019.
- « PREV
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- ...
- 17
- NEXT »