CSVA: 一种全新的二次有机气溶胶化学动力学模式
组内消息 2021-06-11
二次有机气溶胶(SOA)是大气细颗粒物(PM2.5)的重要组分,对能见度和人体健康等有重要影响,在空气污染和全球气候变化中起着关键作用。SOA主要由挥发性有机物(VOC)的降解产物通过气-粒转化生成,其化学成分非常复杂,分子组成往往可达千种。目前SOA演化机制的不确定性,直接制约了正确评估气溶胶对区域空气质量乃至全球气候的贡献影响,因而准确模拟SOA的生成和演化成为全球特别是我国所面临的重要的前沿科学问题。
中科院大气所徐永福课题组通过光化学烟雾箱实验对不同有机物氧化生成SOA的条件和化学反应机制进行了深入研究,如确定了小分子有机物生成SOA的条件和机理,确定了湿度在芳香烃和萜烯类物质生成SOA中的不同作用等。近年来,虽然国内外研究者在SOA成核、传质和老化等方面取得了很多进展,但由于缺乏一种化学动力学模式对各个过程进行耦合和评估,从而导致对SOA的认识存在碎片化的问题。
为了全面了解SOA的生成和演化规律,最近贾龙和徐永福开发了一种基于黏度的二次有机气溶胶核-壳动力学模式(CSVA)。该模式依气溶胶的分子组成将单个颗粒分为核壳两部分,并通过单一方程描述了气-粒转化涉及的气相扩散、界面传质和颗粒相扩散过程(图1),最终用化学反应动力学类似的方程对成核、传质和老化过程进行描述(图2)。烟雾箱实验表明,CSVA可以很好地捕捉以下过程:(1)依赖于湿度的H2SO4-NH3-H2O酸碱成核过程;(2)依赖于颗粒物粒径的无机和有机气溶胶吸湿动力学过程;(3)相对湿度对SOA生成的作用;(4)基于黏度的气溶胶粒径分布特征,等。此外,CSVA模式首次阐明了为什么SOA粒子会由单峰模态演变为双峰模态(图3)的内在机制。
目前国际上仅有个别基于黏度的SOA气-粒传质模型,此类模型假定SOA颗粒为多层和双层结构。这类层结构模型需要耦合各层之间的传质过程,因此极大地增加了模拟复杂度。与之相比,CSVA的结构更清晰和简洁、计算效率更高。这使得CSVA有潜力与其他空气质量模式进行耦合,从而对不同的大气条件下气溶胶演化进行准确模拟。该工作已经在Science of the Total Environment发表。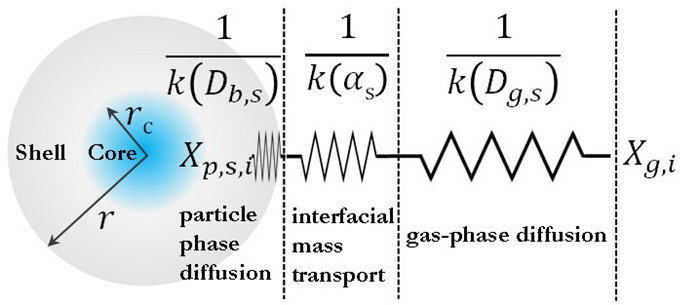
图1. 核-壳结构的单颗粒SOA的传质示意图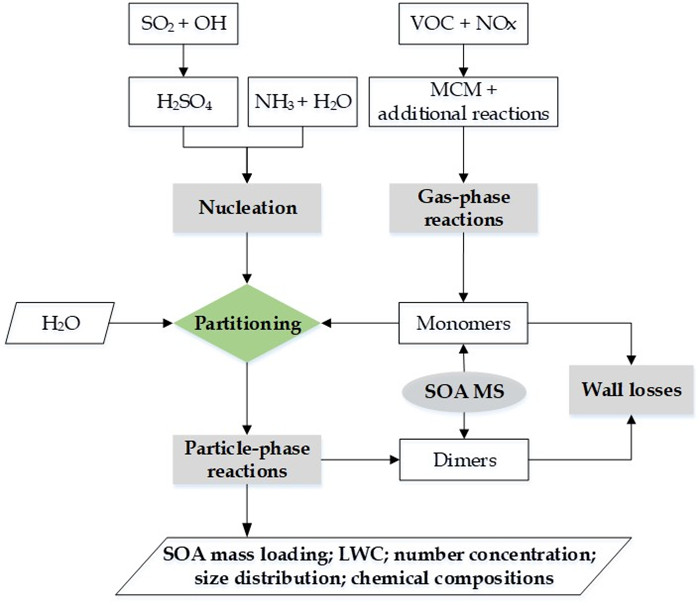
图2. CSVA模式的整体框架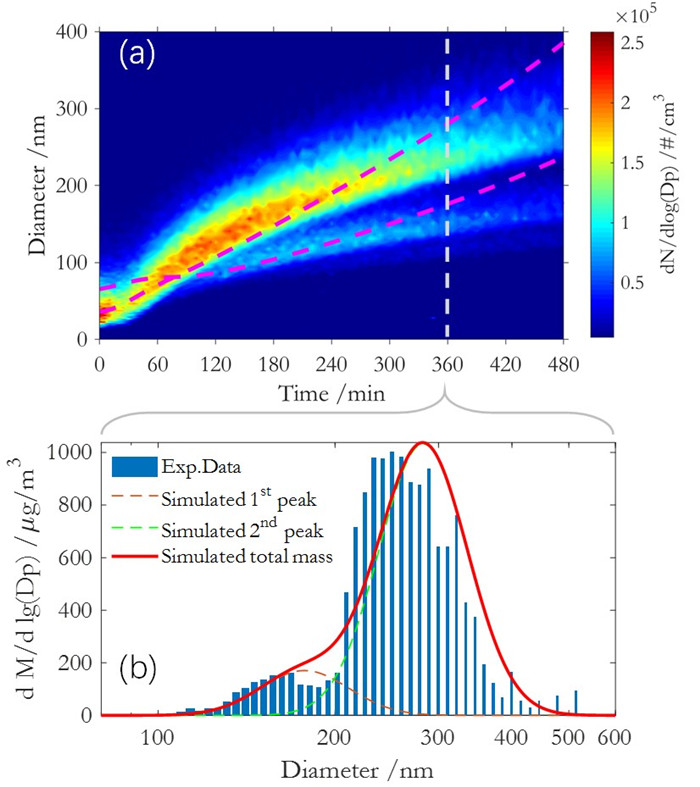
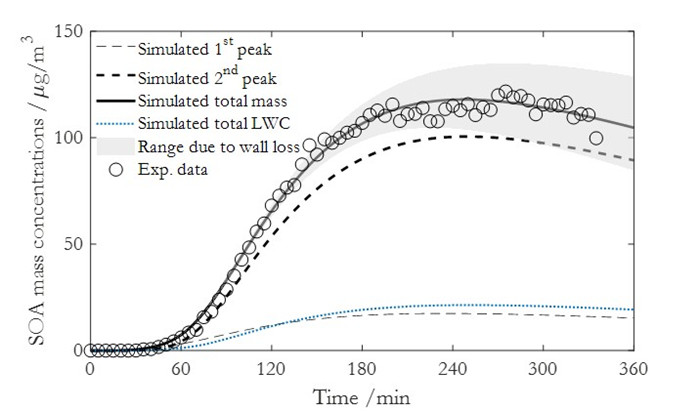
图3.CSVA模拟结果与烟雾箱实验值的比较
Jia, L., Xu, Y.F.*, 2021. A core-shell box model for simulating viscosity dependent secondary organic aerosol (CSVA) and its application. Sci. Total Environ. 789, 147954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147954
Jia, L., Xu, Y.F.*, 2020. The role of functional groups in the understanding of secondary organic aerosol formation mechanism from α-pinene. Sci. Total Environ. 738, 139831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139831
Zhang, Q., Xu, Y.F.*, Jia, L., 2019. Secondary organic aerosol formation from OH-initiated oxidation of m-xylene: effects of relative humidity on yield and chemical composition. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 19, 15007–15021. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-19-15007-2019
Jia, L., Xu, Y.F.*, 2018. Different roles of water in secondary organic aerosol formation from toluene and isoprene. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 18, 8137–8154. https://doi.org/10.5194/acp-18-8137-2018
Ge, S.S., Xu, Y.F.*, Jia, L., 2017. Secondary organic aerosol formation from propylene irradiations in a chamber study. Atmos. Environ. 157, 146–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2017.03.019